China’s Tax Incentives for Small Businesses

Posted by China Briefing Written by Zoey Zhang
We list China’s major tax incentives to foster various types of small businesses.
China is actively creating a friendly environment conducive to the growth of small businesses, taking measures to ease the financial burdens and solve financing difficulties for small and micro firms. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these measures have been further enhanced to help affected firms weather the storm.
In this article, we introduce the major tax incentives for small businesses, including corporate income tax (CIT) cuts for small and low-profit enterprises (SLPEs), individual income tax (IIT) reduction for small business owners, as well as concessions on value-added tax (VAT) and other taxes and fees for small-scale taxpayers and tax measures to lower financing costs of small and micro enterprises.
What are China’s tax incentives for small businesses?
CIT incentives for small and low-profit enterprises
China has recently enhanced its inclusive tax cut policy for small and low-profit enterprises. SLPEs refer to enterprises engaged in non-restrictive and non-prohibited businesses that meet the following three conditions:
- Annual taxable income not exceeding RMB 3 million (approx. US$458,500);
- Number of employees not exceeding 300; and
- Total asset value not exceeding RMB 50 million (approx. US$7.7 million).
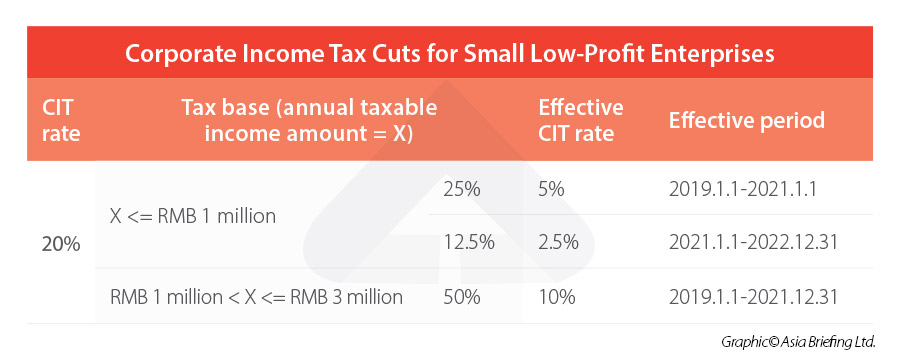
All types of SLPEs in China are able to enjoy a reduced corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 20 percent in combination with a reduction of their tax base.
Specifically, SLPEs are subject to:
- 20 percent CIT rate on 12.5 percent of the taxable income amount for the portion of taxable income not exceeding RMB 1 million (approx. US$152,800) (effective from Jan. 1, 2021-Dec. 31, 2022); and
- 20 percent CIT rate on 50 percent of their taxable income amount for the portion of taxable income more than RMB 1 million but not exceeding RMB 3 million (effective from Jan. 1, 2019-Dec. 31, 2021)
As a result, for an SLPE’s taxable income amount up to RMB 1 million, an effective 2.5 percent CIT rate applies; for the portion of taxable income between RMB 1 million and RMB 3 million, an effective 10 percent CIT rate applies.
Because the SLPE evaluation is carried out at the entity level (instead of at the group level), small subsidiaries of foreign multinational enterprises (MNEs) in China can also benefit from these CIT cuts.
VAT incentives for small-scale taxpayers
China offers value-added tax (VAT) benefits to small-scale taxpayers, including reduced VAT levy rate and increased VAT threshold.
Here, small-scale taxpayers normally refer to taxpayers whose annual VAT taxable sales does not exceed RMB 5 million (approx. US$0.77 million).
However, unincorporated entities, enterprises, and individually owned businesses that do not often incur VAT taxable transactions, even if their annual taxable sales exceed the stipulated standard, can choose to be treated as small-scale taxpayers (instead of being registered as general taxpayers).
Reduced VAT rates
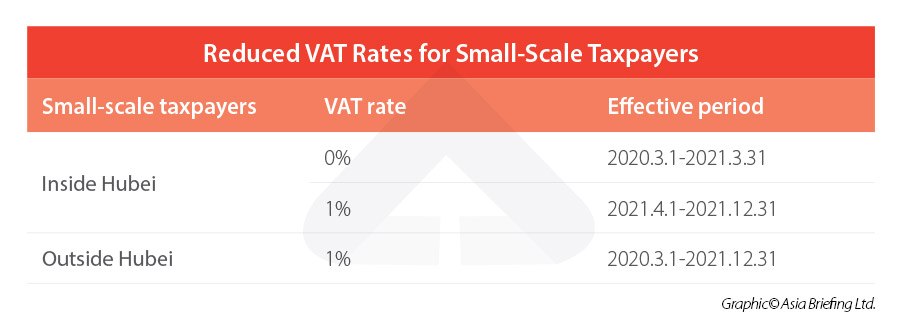
Since the first COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan city, China exempted small-scale taxpayers in Hubei province from paying VAT and reduced VAT for small-scale taxpayers in the other regions. But as the pandemic receded, this preferential tax policy is tightened.
Currently, from April 1, 2021 through December 31, 2021, all small-scale VAT taxpayers (both in Hubei or outside Hubei), to which a VAT levy rate of 3 percent is applicable, can pay VAT at the reduced levy rate of 1 percent; they may also prepay VAT at the reduced pre-levy rate of 1 percent for their items subject to a pre-levy rate of 3 percent.
Increased VAT threshold
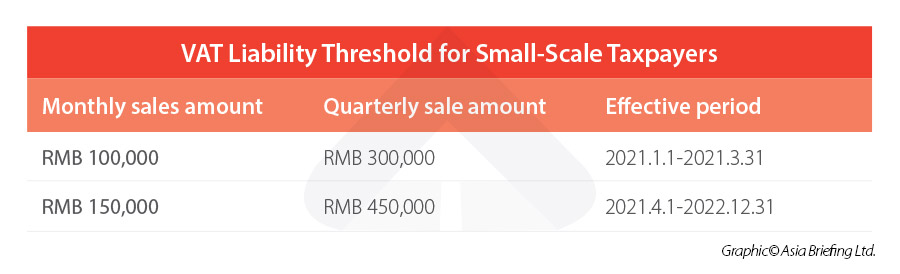
China also raised the VAT exemption threshold for small-scale VAT taxpayers from April 1, 2021 to December 31, 2022. The VAT threshold for small-scale taxpayers has been lifted to RMB 150,000 (approx. US$23,240) per month (or RMB 450,000 per quarter, approx. US$69,700) from the previous RMB 100,000 (approx. US$15,200) per month (or RMB 300,000 per quarter, approx. US$45,800).
In other words, if the monthly sales amount of the small-scale taxpayer is under RMB 150,000 (or the quarterly sales amount is under RMB 450,000 for taxpayers who choose one quarter as a tax payment period), the taxpayer will not be subject to VAT.
There is one situation where the taxpayer with monthly sales of over RMB 150,000 can still be exempt from VAT. That is when the taxpayer occasionally occurs real estate transactions that month. Some small-scale taxpayers have the obligation to pre-pay VAT tax. The policy has clarified that if their monthly sales in the place where the VAT needs to be pre-paid do not exceed RMB 150,000, they are not required to pre-pay VAT.
The state tax authority has clarified that if a small-scale taxpayer with total monthly sales of more than RMB 150,000, but after deducting the sales of real estate, other sales (i.e., the sales of goods, labor, services, and intangible assets) do not exceed RMB 150,000, the small-scale taxpayer can still be exempt from VAT.
Education surcharge and other tax reduction
China’s national and local education surcharges are calculated based on a taxpayer’s actual payment of VAT and consumption tax.
At present taxpayers whose sales amount does not exceed RMB 100,000 per month (or RMB 300,000 per quarter) will be exempt from education surcharge, local education surcharge, and water conservancy construction fund.
As mentioned above, since April 1 this year, the VAT threshold for small-scale taxpayers has been lifted to RMB 150,000/month (or RMB 450,000/quarter). However, taxpayers should note that the new VAT threshold will not affect the payment of education surcharge unless the relevant policy is updated.
Aside from the exemption of education surcharges, taxpayers can keep an eye on additional tax and fee relief offered locally.
Local governments are granted authority to reduce levying of six types of taxes and two fees on small-scale taxpayers within the tax base of 50 percent. The six taxes and two fees refer to resource tax, urban maintenance and construction tax, property tax, urban land use tax, stamp duty (excluding stamp duty on securities transactions), arable land use tax, education surcharge, and local education surcharge.
IIT incentives for small business owners
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2022, during which period individually owned businesses, sole proprietorships, and partnership enterprises can enjoy some individual income tax (IIT) relief.
For the portion of an individually owned business’ income from a business operation that does not exceed RMB 1 million, the business is entitled to a 50 percent reduction of IIT on the basis of the prevailing incentives.
From April 1, 2021, individually owned businesses, sole proprietorship enterprises, partnership enterprises, and individuals will no longer be required to pre-pay IIT at the time of issuance of cargo transport VAT invoices on behalf.
Tax measures to lower financing costs of small businesses
To help small and micro enterprise raise funds, China exempts financial institutions from paying VAT on their interest income derived from small loans to farmers, small enterprises, micro enterprises, and individually owned businesses. Besides, loan contracts signed between small or micro enterprises and financial institutions are exempt from stamp duty.
Both measures are effective until December 31, 2023.
This article was originally included in the China Briefing Magazine issue Tax Incentive in China.
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at [email protected].
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.